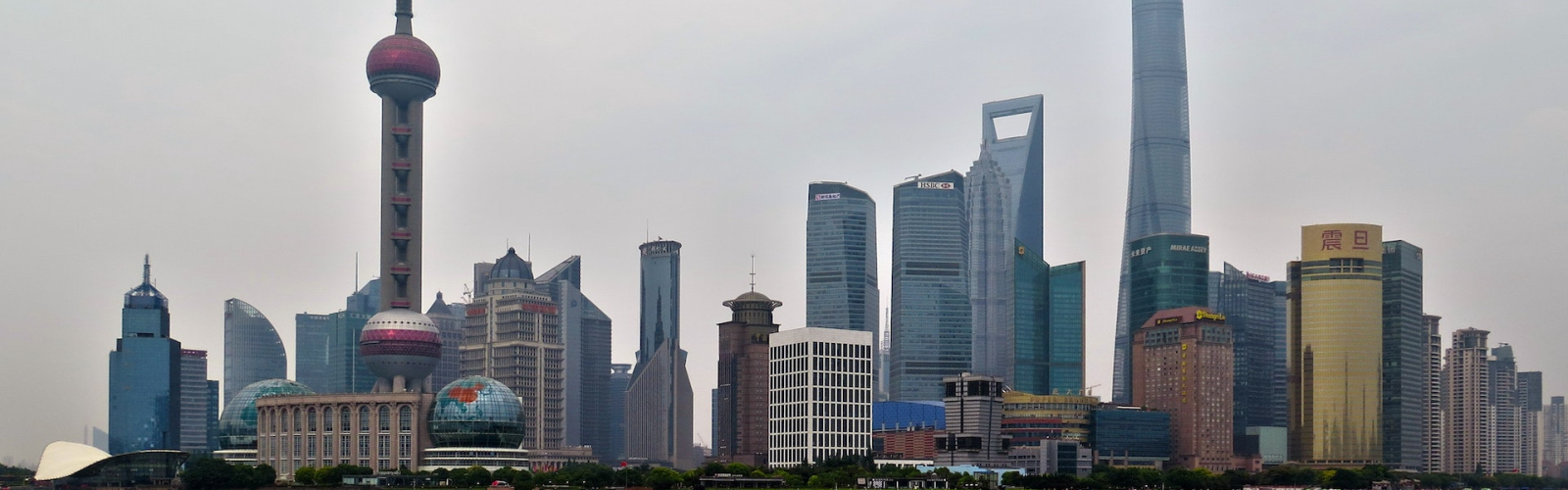
Over the past decade, China’s relentless drive toward technological advancement has become a defining narrative in both its policy and culture. From e-commerce booms to smart cities, the nation's digital infrastructure underpins its modern resurgence on the global stage. Now, China stands at the forefront of another revolutionary leap—5G Advanced, also known as 5.5G. This new phase of mobile connectivity promises speeds and capabilities eclipsing what 5G previously offered, with profound impacts across politics, economy, public life, and traditional culture. But what exactly is 5.5G? How is China deploying it? And what might it mean for the country’s future? Dive in as we explore how 5G Advanced is pushing the boundaries of connectivity in China.
Understanding 5G Advanced
For many, the arrival of 5G in recent years already feels like yesterday’s news. Cities in China have been enjoying rapid smartphone download speeds, buffer-free video calls, and smarter, sensor-driven public spaces for several years. However, relentless innovation never rests. The development of 5G Advanced (5.5G) is not simply an incremental upgrade but a new technological chapter that bridges 5G and the future aspirations of 6G networks.
Officially termed as “5G-A” or 5.5G, this technology enhances the performance of existing 5G infrastructure while introducing fresh capabilities:
- Peak download speeds: Up to 10 gigabits per second, far beyond current 5G rates.
- Massive device connectivity: Supporting up to 1 million devices per square kilometer.
- Enhanced uplink rates: Making real-time remote control and industry automation more feasible.
- Reduced latency: Bringing delay almost to negligible levels, vital for mission-critical applications such as precision medical surgery.
- Green and energy-efficient: Smarter network algorithms drastically reduce energy consumption per bit of data.
In short, 5.5G addresses not only consumer smartphone needs but underpins China’s ambitions in areas like autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, smart metropolises, and rural revitalization.
China’s 5.5G Rollout
Chinese policymakers have consistently made telecom infrastructure a linchpin of national strategy. According to the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT), China ended 2023 with over 3 million 5G base stations, representing more than half of the global total. Key players like China Mobile, China Unicom, and China Telecom have actively piloted and commercialized 5.5G in major cities since early 2024.
The government supports this push through the “New Infrastructure” initiative, funnelling investment into artificial intelligence, industrial internet, ultra-high voltage power grids, and next-generation telecom networks. Provincial-level policies also stimulate local innovation, urging industries, universities, and local governments to collaborate closely with telecom giants and tech firms such as Huawei and ZTE.
The First Urban Pilots
Early pilots have appeared in innovation centers like Shanghai, Shenzhen, Beijing, and Hangzhou. Shanghai, for example, launched its “5.5G City” initiative in mid-2024, enabling applications such as:
- Ultra-HD 8K livestreaming of cultural and sporting events
- AI-powered transportation management and autonomous bus lanes
- Remote real-time medical consultations surpassing previous fidelity limits
- Smart factory automation, where robots and humans work seamlessly together
In rural regions, 5.5G facilitates precision agriculture through sensor networks and drone coordination, narrowing the digital divide and helping protect China’s unique ecological environments.
Economic and Social Impacts
Beyond the technical promise, the rollout of 5G Advanced acts as a catalyst for economic and societal change. The Chinese government estimates that next-generation networks will add over 3 trillion yuan (approx. $415 billion USD) to the country’s GDP by 2025. Let’s break down this impact:
1. Economy and Manufacturing
Ultra-reliable low-latency connectivity enables the growth of “smart manufacturing” and digital supply chains. Factories now deploy thousands of sensors to optimize output, cut waste, and ensure product quality. 5.5G isn’t just faster—it’s more precise and efficient, paving the way for real-time machine collaboration and adaptive production lines. China’s position as the “world’s factory” is strengthened by deploying these capabilities nationwide, not merely in coastal megacities.
2. Tourism, Ecological Protection, and Rural Revitalization
With 5.5G, China leverages digital tech to enhance tourist experiences through augmented reality (AR) guides, real-time translation, and virtual tours, opening new vistas for heritage appreciation. Preservationists use drones and data analytics to monitor fragile zones of UNESCO heritage sites, and smart parks can proactively detect environmental hazards. In this way, 5.5G helps protect cultural and historical legacies, much as ancient medical traditions in India have preserved centuries of wisdom through adaptation and innovation. In the countryside, 5.5G-enabled platforms support online agricultural marketplaces and live rural education, giving villagers new tools to connect with markets and culture.
3. Traditional Culture in a Hyperconnected Age
Interestingly, one outcome of advanced connectivity is the revival and reimagination of traditional Chinese culture. Through immersive live-stream performances, digitized museum exhibits, and collaborative virtual festivals, China’s living heritage reaches new generations at home and abroad. Much like crafting a powerful narrative, understanding how to share cultural stories online requires creativity and structure, principles also reflected in successful content creation strategies that bridge tradition with technology. 5.5G’s capacity for massive synchronous livestreams with ultra-realistic visuals helps remote temples, minority villages, and folk artists share their stories on a national—and even global—scale.
4. Politics and Governance
The rollout of 5.5G supports China’s “Digital China” strategy, strengthening urban and provincial governance. Smart traffic management, digital public health, and real-time environmental monitoring curb pollution and keep megacities running. Enhanced digital infrastructure also supports agile responses to emergencies, reflecting the government’s commitment to delivering both efficiency and safety. These technological strides also reflect deeper political challenges in China, where governance must continually adapt to new expectations in transparency, efficiency, and social engagement.
Challenges and Debates: Navigating the Road Ahead
Yet, as with any major technological leap, challenges and debate remain. Some worry about issues such as data privacy, cybersecurity, and the potential for digital overreach. Rural regions, despite rapid progress, still face hurdles in funding and technical talent. Moreover, energy usage in expanding data centers poses ecological questions: Is “green 5G” green enough? The government and leading companies continue to stress the importance of ethical, inclusive, and sustainable 5.5G integration, seeking to balance growth with social responsibility.
Conclusion: The New Silk Road of Data
China’s embrace of 5G Advanced (5.5G) is far more than a matter of faster internet speeds—it heralds an age in which digital connectivity is interwoven with every aspect of society: from high-tech industries to rural villages, ancient temples to tomorrow’s smart cities. This bold step forward opens new avenues for economic development, cultural innovation, ecological stewardship, and international collaboration under the banner of a “digital Silk Road.”
As China continues to lead in 5.5G innovation, the world is watching closely. The country’s unique synthesis of policy direction, public ambition, and technological prowess ensures that the story of 5G Advanced is as much about society and culture as about cables and code. Whether you’re a policy enthusiast, a tech lover, a student of Chinese culture, or a visitor eager to experience China’s next big leap, you are witnessing a moment when the boundaries of connectivity are pushed—and the future is closer than ever.








